Analyzing big data is crucial for organizations to make smarter data-driven decisions—but not all big data is created equally. It’s important to make the distinction between structured data and unstructured data:
- Structured data is information that follows a highly organized, predefined schema, making it easy to search through and query. If it can fit inside a relational database or Excel spreadsheet with intersecting rows and columns, it’s structured data.
- Unstructured data is any information that doesn’t fall into the neat categories of structured data. Examples of unstructured data include text, images, and audio files.
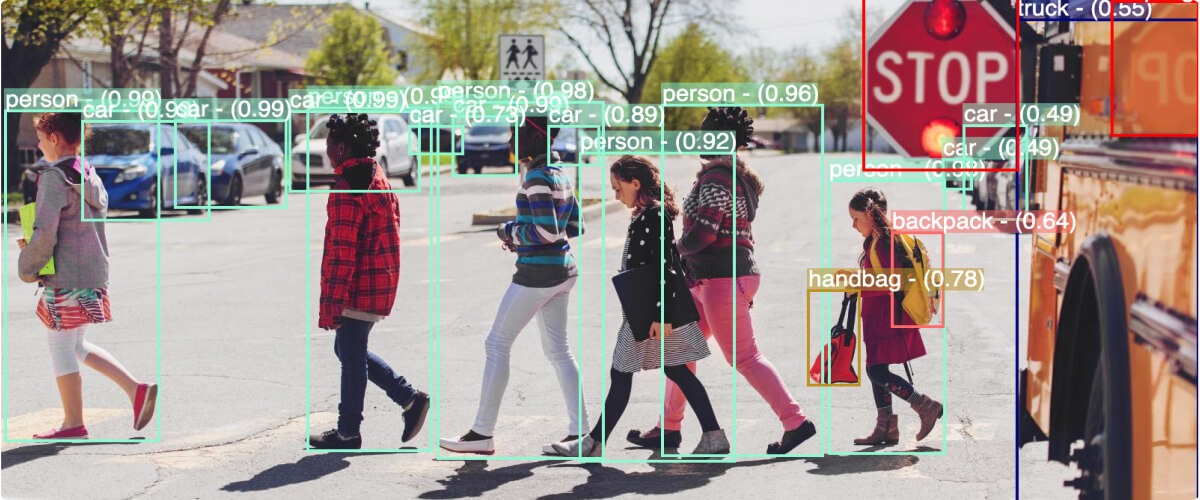
In particular, videos are a prime example of unstructured data. Rather than the digital bits and bytes that make up video files, what’s really of interest is high-level information about what the video contains and depicts—from using facial recognition on individuals who appear in the video to detecting dangerous events with fire detection and fall detection.
But how can you extract this information in an automated, efficient manner? In other words, how can you turn videos into structured data?
How to Create Structured Data from Videos
To create structured data from videos, organizations are using sophisticated computer vision and artificial intelligence techniques. Computer vision platforms like Chooch can help anyone build state-of-the-art AI models that analyze videos frame by frame, detecting the people, objects, or events that you’ve trained them to look for.
Once you’ve gone through the AI training process, your computer vision model can automatically annotate each frame of the video. AI models can detect the motion of a person or object throughout the scene, as well as detect various actions and events. These annotations, which are saved as structured data, can then be searched and queried to retrieve the most relevant parts of the video.
Use Cases of Computer Vision for Video Data
- Media AI: Computer vision has a wide range of applications in the media and entertainment industries. For example, you can automatically tag the objects in a livestream video, allowing for better targeted advertising. You can also perform facial recognition on the people (e.g., celebrities) in a video, making it easier for people to find who and what they’re looking for.
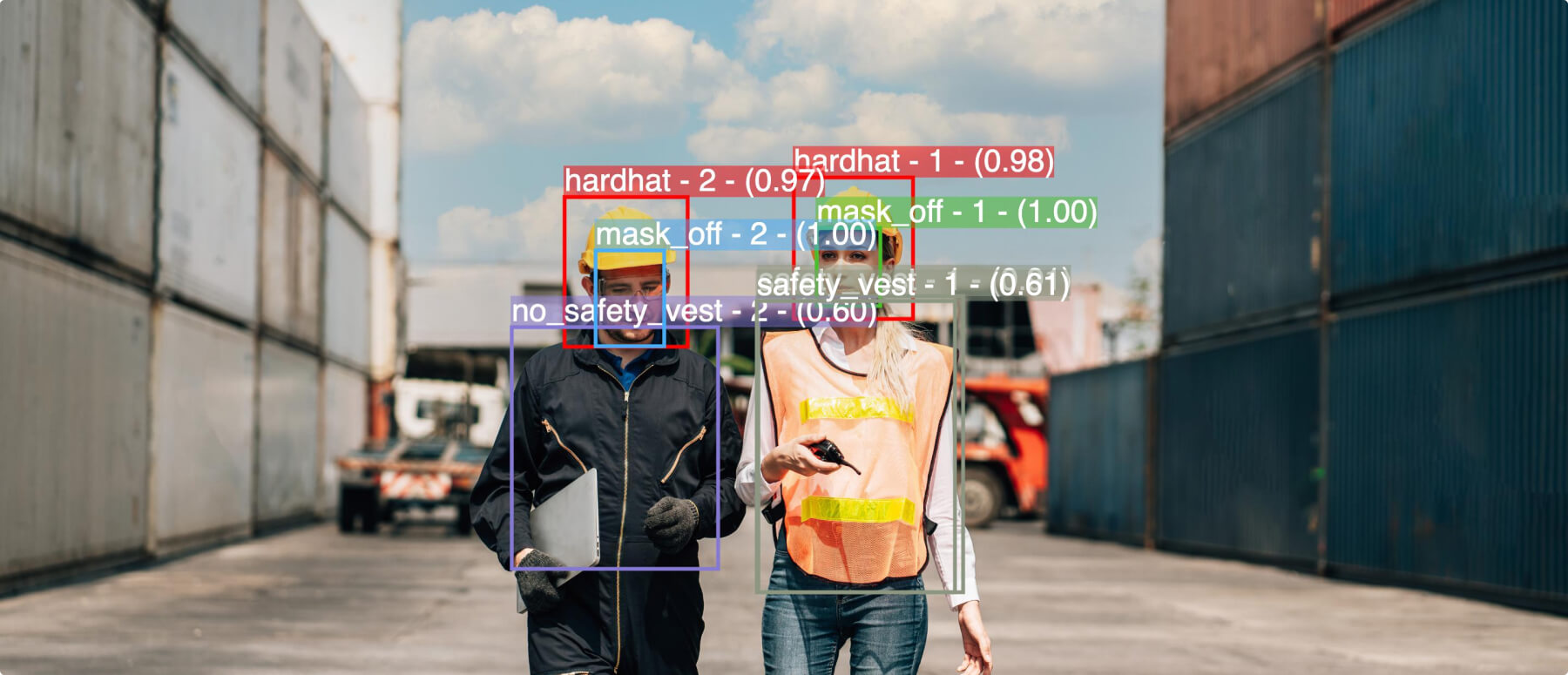
- Safety & Security AI: In the field of safety and security, computer vision can help protect public spaces from threats and dangers. Facial recognition models can confirm that an individual is authorized to access the premises, while PPE detection models can make sure that workers are wearing the appropriate clothing and equipment on the job.
- Geospatial AI: Computer vision models can efficiently analyze drone and satellite images and videos. For example, you can train an AI model to detect wildfires, analyze drought or industrial activity levels, identify different animal species, and much more.
Conclusion
It’s now easier than ever for your unstructured video data to become structured, thanks to computer vision and AI. Want to learn more about how Chooch can help? Get in touch with Chooch’s team of computer vision experts for an AI demo.